Compliance
1. Introduction
1.1 What is an ISMS?
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a structured framework of policies, processes, and controls designed to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s information. It helps systematically manage and reduce the risks related to information security, ensuring that sensitive data – such as customer details, financial records, and intellectual property – is adequately protected.
1.2 Why do we need an ISMS?
Information is one of the organization's most valuable assets. With increasing cyber threats, regulatory demands, and the need to protect customer trust, safeguarding information has never been more critical. An ISMS provides a proactive approach to protecting data, ensuring the organization can:
- Comply with legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements.
- Protect against data breaches, cyberattacks, and accidental loss of information.
- Ensure business continuity in the event of a disruption or security incident.
- Build and maintain trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
The ISMS works through a risk-based approach, meaning it identifies risks to information security and implements controls to manage those risks. It follows a continuous cycle of improvement known as Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA).
1.3 How does it work?
- Plan: Identify risks and set objectives for addressing them.
- Do: Implement the necessary security measures and controls.
- Check: Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the security measures.
- Act: Make improvements based on assessments and emerging risks.
The ISMS is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process that adapts to changes in the business, technology, and external threats.
1.4 Alignment with ISO/IEC 27001
The ISMS is aligned with the internationally recognized ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard. This standard provides a best-practice framework for managing information security. By adhering to ISO/IEC 27001, the organization demonstrates its commitment to:
- Global best practices in information security management.
- Ensuring compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Continuous improvement in managing information security risks and safeguarding critical information assets.
ISO/IEC 27001 requires organizations to take a systematic approach to managing sensitive information and ensuring that security measures are continually reviewed, improved, and updated. Our ISMS helps us meet these requirements by integrating security into every part of the business, from IT infrastructure to human resources and operations.
1.5 Resources
water IT Security GmbH's ISMS Team will receive comprehensive resources such as experienced employees, tools, additional training and best practices tailored to different roles and responsibilities to uphold the standards of security excellence. The goal is to ensure that every member of the organization is equipped with the necessary resources to effectively safeguard sensitive data, mitigate risks and contribute to a culture of security awareness.
1.6 Management Commitment
Information security is a management responsibility, and decision-making for information security is not delegated. While specialists and advisors play an important role in helping to make sure that controls are designed properly, functioning properly and adhered to consistently, it is the manager in charge of the business area involved who is primarily responsible for information security.
Primary Departments Working on Information Security - Guidance, direction and authority for information security activities are centralized for all water IT Security GmbH organizational units in the Information Security Program and summarized in this document. water IT Security GmbH management is responsible for establishing and maintaining organization-wide information security policies, standards, guidelines and procedures.
Compliance checking to ensure that organizational units are operating in a manner consistent with these requirements is the responsibility of department managers. Investigations of system intrusions and other information security incidents are the responsibility of the InfoSec Team. Disciplinary matters resulting from violations of information security requirements are handled by CISO working in conjunction with the HR department.
2. Purpose
The purpose of this policy is to establish the organization’s commitment to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of its information assets. This policy serves as the foundation of the Information Security Management System (ISMS) and ensures alignment with business objectives, legal and regulatory requirements, and industry best practices in accordance with ISO/IEC 27001:2022.
3. ISMS Activities
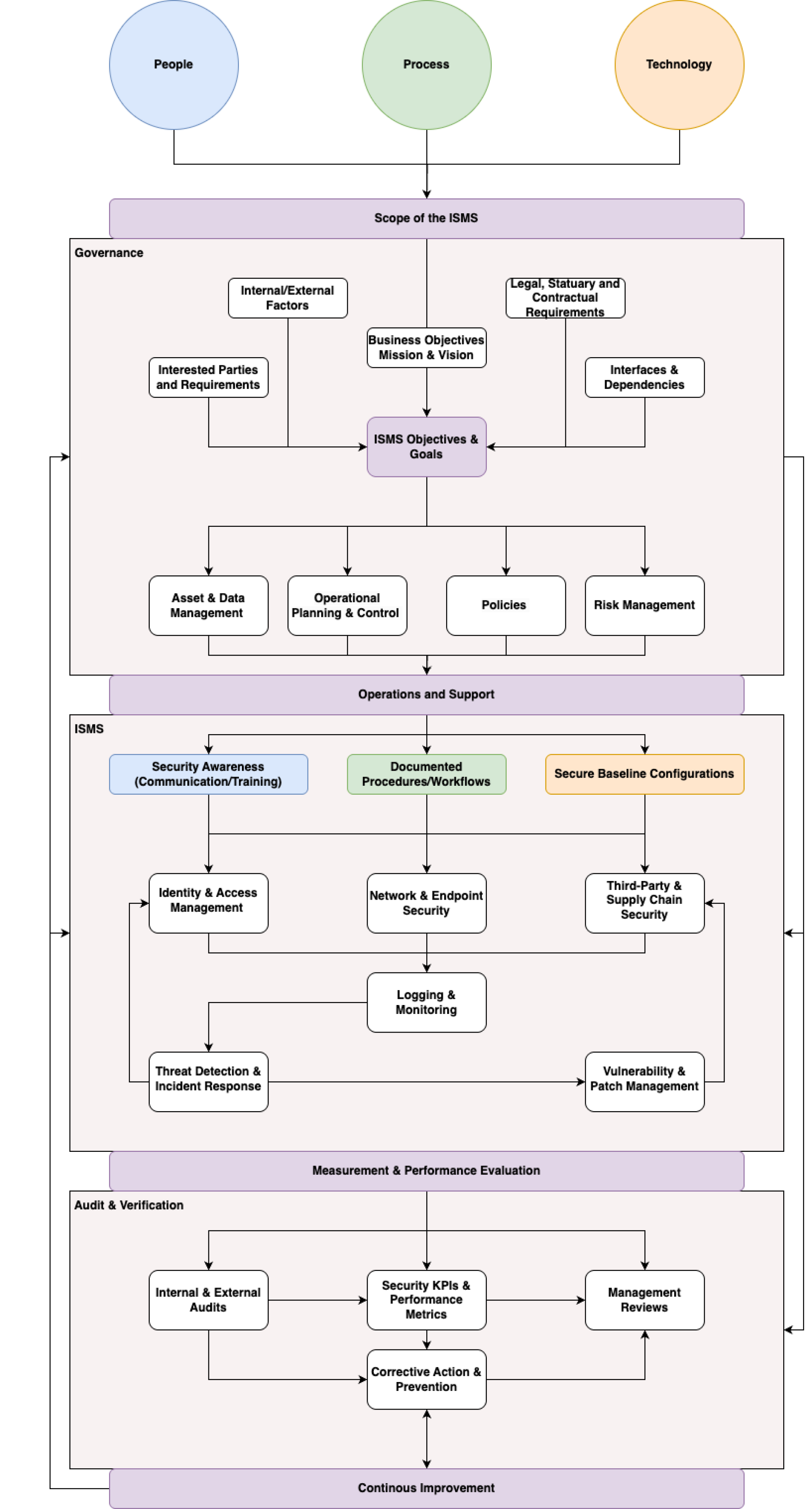
The ISMS activities are based on the GOV-1 Context, Requirements & Scope. The scope defines the core processes, technology aspects, people and exclusions of the ISMS. It results in a governance framework which takes internal & external factors, interested parties, business objectives, legal requirements and interfaces & dependencies into consideration.
Based on these factors, the Information Security Objectives got identified and described. They provide the higher level direction for the ISMS operations.
4. Review and Maintenance
This Information Security Policy will be reviewed at least annually, or when significant changes occur in the organization’s business environment, regulatory landscape, or operational structure. The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), along with Top management, will be responsible for ensuring the policy remains current and aligned with business goals and evolving security threats. Revisions and updates will be documented in the version and approval history.
5. Information Security Objectives
The organization is committed to achieving the following information security objectives:
Information Security Objective | Description |
| Confidentiality | Ensure that sensitive data is accessible only to authorized individuals or systems. |
| Integrity | Ensure the accuracy and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle. |
| Availability | Securing availability of provided services, and data through business continuity measures. |
| Risk Reduction | Minimizing security risks and protecting business continuity. |
| Compliance | Ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulations. |
| Continuous Improvement | Ensures the ISMS evolves to respond to new threats, incidents, and opportunities for enhancement. |
| Process Standardization | Improving processes by reducing manual efforts and creating standardized procedures. |
| Increased Awareness | Conduct frequent information security awareness training. |
6. Information Security Principles
The organization’s information security strategy is based on the following principles:
- Risk-Based Approach: Information security measures will be proportionate to the risks identified through regular risk assessments.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: The organization will comply with all applicable laws, regulations, and contractual requirements.
- Leadership Commitment: Top management will actively support and provide resources for the ISMS.
- User Awareness: Employees, contractors, and third parties will receive appropriate security training and awareness.
- Continuous Improvement: The ISMS will be regularly reviewed and improved to adapt to changing threats and organizational needs.
7. Roles and Responsibilities
Information security is the responsibility of every employee, contractor, and third party. Specific roles and responsibilities include:
GOV-2 Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities
Role | Responsibilities | Authority | Competencies |
Top Management | Approves capital expenditures related to information security, defines ISMS strategy, communicates with senior management, aligns policies with organizational goals, allocates resources, and reviews ISMS performance. | Strategic decisionmaking, ISMS strategy, and investments. |
|
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) | Oversees and manages ISMS, conducts risk assessments, manages security incidents, ensures compliance with laws and standards (such as ISO 27001), trains staff on security practices. | Enforce security measures, escalate issues to top management. |
|
ISMS Team | Reviews and advises on ISMS activities and strategy, assesses incidents, recommends improvements to management, and ensures security measures are implemented effectively.
| Provide ISMS recommendations to management and oversee security improvements. |
|
Department Heads | Ensure department compliance with ISMS, report security risks, communicate security policies to staff. | Enforce compliance in their department, manage department-specific risks. |
|
Tenant Manager | Ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of designated systems, conduct access reviews, and implement security controls. | Authority to enforce security measures for assigned systems. |
|
Internal IT | Ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of end devices and implements security controls. | Authority to enforce security measures for endpoints. |
|
Internal Auditors | Conduct audits to ensure ISMS compliance, report findings to management, and collaborate with external auditors. | Independent audit authority. May be provided from an outside organization. |
|
Solution Lead SOC | Coordinate and lead response to security incidents, manage incident documentation, and ensure effective communication. | Initiate and lead incident response actions. |
|
Data Privacy Officer (DPO) | Ensure compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR), advise on privacy issues, monitor data privacy practices, and liaise with regulatory authorities as needed. | Authority in data privacy matters. |
|
AI Commissioner | Oversight and control of the ethical, legal, and regulatory aspects of artificial intelligence to ensure its responsible development and deployment. Protection of public interests by setting guidelines, enforcing compliance, and addressing risks related to AI governance, privacy, and bias. | Authority in AI matters. |
|
Training and Awareness Team | Develop and deliver security training and awareness programs for employees and contractors. comprises
| Authority to coordinate training sessions and update awareness materials. |
|
Third Parties and Contractors | Comply with security requirements, protect primary assets, report breaches. | Limited authority based on contractual obligations. |
|
All Employees | Follow security policies, report incidents, attend security training, secure workstations, acknowledge policies. | Report security incidents and escalate concerns. |
|
Asset & Risk Owners | Ensure the safeguarding of assets and associated risks in compliance with applicable information security policies and procedures. | Apply secure configurations, perform regular reviews of ACLs and configurations. Frequently report risk status to CISO and top management. |
|
Office Managers | Manages building access and provides tokens. | Authority to enforce security measures for physical locations. |
|
8. Policy Statements
8.1 Risk Management
The organization will identify, assess, and manage risks to its information assets through a formal risk management process. This process includes:
- Regular risk assessments to evaluate and categorize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Risk treatment plans that outline mitigation strategies, including risk acceptance, reduction, avoidance, and transfer, in accordance with the risk management policy.
- Continuous monitoring of the risk environment to address emerging threats.
8.2 Compliance
The organization will comply with all relevant legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements. Regular audits will ensure ongoing compliance, and nonconformities will be addressed through corrective actions.
8.3 Asset Management
The organization will identify, document, and classify all information assets based on their sensitivity and importance to the business. Appropriate controls will be applied throughout the asset lifecycle (e.g., from creation to disposal) to ensure data protection.
8.4 Access Control
Access to the organization’s information systems and data will be based on the principle of least privilege. Access rights will be reviewed regularly to ensure that users have only the permissions necessary to perform their job functions. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other access control measures will be implemented where applicable.
8.5 Incident Management
The organization will maintain an incident management process for the identification, reporting, and resolution of information security incidents. Employees and third parties are required to report security incidents immediately to the CISO. The organization will conduct root cause analysis and lessons-learned exercises to improve its incident response capability.
8.6 Business Continuity
The organization will develop and maintain a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) and Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) to ensure that critical business functions can continue in the event of a security incident or major disruption. These plans will be tested regularly, and results will be used to improve the effectiveness of the continuity strategy.
8.7 Monitoring and Improvement
The ISMS will be monitored through regular internal audits, reviews, and assessments to ensure its continued effectiveness and compliance with this policy. Weaknesses identified through these processes will be addressed through corrective actions and continuous improvement initiatives.
8.8 Vulnerability Management
The organization implements a comprehensive vulnerability management process to safeguard its systems against potential risks. Vulnerabilities in critical systems, networks, and applications are identified through quarterly vulnerability scans. Automated tools are utilized for continuous monitoring to detect emerging threats in real-time. Once vulnerabilities are identified, they are promptly addressed through an established patch management process. All findings, actions, and outcomes are thoroughly documented for tracking and future audits, ensuring transparency and compliance.
8.9 Security Awareness Training
Security awareness is vital for fostering a culture of vigilance within the organization. Annual training sessions are conducted for all employees, focusing on topics like phishing prevention, strong password practices, and incident reporting protocols. To reinforce these lessons, the organization uses simulated phishing attacks and quizzes to evaluate employee understanding. Training materials are regularly updated to address emerging threats and trends, ensuring that employees are equipped with the knowledge to mitigate risks effectively. Role-specific training programs are also offered, tailoring content to the unique security responsibilities of different roles.
8.10 Vendor and Third-Party Management
Vendors and third-party partners are integral to the organization’s operations, and their security practices directly impact the organization’s risk profile. During the onboarding process, each vendor undergoes a thorough assessment to evaluate their security measures and compliance with organizational standards. Contracts include explicit security requirements, such as data protection obligations and incident management protocols. Regular risk evaluations are conducted to ensure vendors maintain compliance over time, and vendors are required to report any security incidents promptly. The organization collaborates with its partners to mitigate risks effectively and uphold a secure operational environment.
8.11 Physical Security
To ensure the safety of the organization’s physical assets, strict security measures are enforced. Access to facilities is controlled through the use of electronic key cards and biometric authentication systems for restricted areas. Visitor access is managed through a detailed logging process, and all entries and exits are monitored. A clean desk policy mandates that sensitive information must not be left unsecured, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. High-risk areas are equipped with CCTV systems to deter unauthorized activities and document incidents. Additionally, environmental controls, such as fire suppression systems and climate control, are implemented to protect critical infrastructure.
9. Violations and Enforcement
The policy is enforced by the ISMS Team. All employees and contractors must strictly adhere to these guidelines. Nonadherence to this policy will be subject to disciplinary actions. Any breaches or suspected violations must be reported immediately to the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) and will be treated based on the disciplinary process of sanctions policy.
If you have any questions regarding the ISMS at water IT Security GmbH, please contact hello@water-security.de
